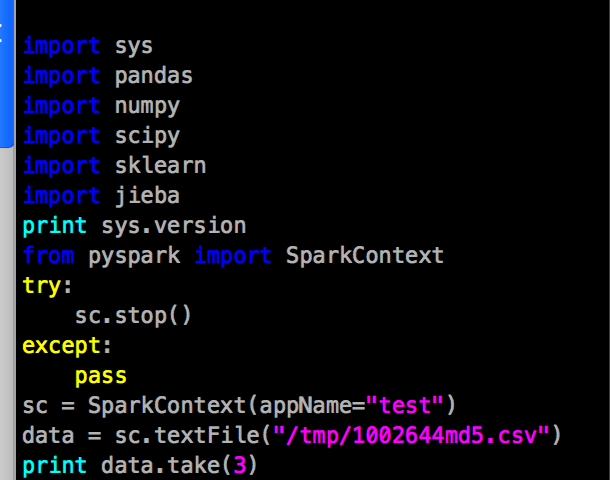
Since I didn’t spend much time on hadoop and spark maintaince, our first party would like to use jupyterhub/lab on hadoop, and their cluster was enhanced security with kerberos and hdfs encryption, so I have to modify jupyterhub/lab to adapt the cluster job submission.
The first party firstly wants to use the SSO login, and somedays they want to use linux pam users to login, so I wrote a custom authenticator to use linux pam login and use the keytab with linux username to authenticate from kerberos in jupyterhub. So the customers could submit their hive or spark jobs without kinit command.
Firstly, the keytab of each user has a fixed filename convention, such as , a principal on dmp-python1 host, would like xianglei/dmp-python1@GC.COM, and the keytab file should be xianglei.py1.keytab.
And then, the login handler in jupyterhub is jupyterhub/handlers/login.py
change the login.py to login and request a username from customer’s SSO system.
class LoginHandler(BaseHandler):
"""Render the login page."""
# commented for matrix ai
args = dict()
args['contenttype'] = 'application/json'
args['app'] = 'dmp-jupyterhub'
args['subkey'] = 'xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx'
def _render(self, login_error=None, username=None):
return self.render_template(
'login.html',
next=url_escape(self.get_argument('next', default='')),
username=username,
login_error=login_error,
custom_html=self.authenticator.custom_html,
login_url=self.settings['login_url'],
authenticator_login_url=url_concat(
self.authenticator.login_url(self.hub.base_url),
{'next': self.get_argument('next', '')},
),
)
async def get(self):
"""
modify to fit pg's customized oauth2 system, if this method publish with matrix ai, then comment all,
and write code that only get username from matrixai login form.
"""
self.statsd.incr('login.request')
user = self.current_user
if user:
# set new login cookie
# because single-user cookie may have been cleared or incorrect
# if user exists, set a cookie and jump to next url
self.set_login_cookie(user)
self.redirect(self.get_next_url(user), permanent=False)
else:
# if user doesnt exists, jump to login page
'''
# below is original jupyterhub login, commented
if self.authenticator.auto_login:
auto_login_url = self.authenticator.login_url(self.hub.base_url)
if auto_login_url == self.settings['login_url']:
# auto_login without a custom login handler
# means that auth info is already in the request
# (e.g. REMOTE_USER header)
user = await self.login_user()
if user is None:
# auto_login failed, just 403
raise web.HTTPError(403)
else:
self.redirect(self.get_next_url(user))
else:
if self.get_argument('next', default=False):
auto_login_url = url_concat(
auto_login_url, {'next': self.get_next_url()}
)
self.redirect(auto_login_url)
return
username = self.get_argument('username', default='')
self.finish(self._render(username=username))
'''
# below is cusstomized login get
import json
import requests
access_token = self.get_cookie('access_token') # this is the oauth2 access_token
self.log.info("access_token: " + access_token)
token_type = self.get_argument('token_type', 'Bearer')
if access_token != '':
# use token to request sso address, to get ShortName ShortName is used for kerberos
userinfo_url = 'https://xxxx.com/paas-ssofed/v3/token/userinfo'
headers = {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key': self.args['subkey'],
'Auth-Type': 'ssofed',
'Authorization': token_type + ' ' + access_token
}
body = {
'token': access_token
}
resp = json.loads(requests.post(userinfo_url, headers=headers, data=body).text)
user = resp['ShortName']
data = dict()
data['username'] = user
data['password'] = ''
# put ShortName into python dict, and call login_user method of jupyterhub
user = await self.login_user(data)
self.set_cookie('username', resp['ShortName'])
self.set_login_cookie(user)
self.redirect(self.get_next_url(user))
else:
self.redirect('http://xxxx.cn:3000/')Do not change the post method of LoginHandler
And then, wrote a custom authenticator class, I named it as GCAuthenticator, it do nothing, just return the username from LoginHandler.And put the file into jupyterhub/garbage_customer/gcauthenticator.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
from tornado import gen
from jupyterhub.auth import Authenticator
class GCAuthenticator(Authenticator):
"""
usage:
1. generate hub config file with command
jupyterhub --generate-config /path/to/store/jupyterhub_config.py
2. edit config file, comment
# c.JupyterHub.authenticator_class = 'jupyterhub.auth.PAMAuthenticator'
and write a new line
c.JupyterHub.authenticator_class = 'jupyterhub.garbage_customer.gcauthenticator.GCAuthenticator
"""
@gen.coroutine
# 入口参数固定写法, 啥也不做, 直接返回用户名, 即为真.这里传递的data, 就是之前在login里面定义的data['username']和data['password']
# 但是由于验证已经由甲方的sso做了, 所以我们用不到password, 但是格式还是要遵守的.
# 其实按照这个思路, 自己把这个方法改写成mysql, postgres, 或者文本文件做用户验证, 其实也很简单.
def authenticate(self, handler, data):
user = data['username']
return user
And then, the local kerberos authentication step.
When login successed, jupyterhub will call spawner method in spawner.py to fork a sub process, the spawner method will call singleuserapp method to create a sub process of notebook and in system process, it will named as singleuser. But actually, the subprocess is created by spawner, so I should extend the spawner method, then I can use the kerberos authenticate and insert the environment variables, this step didn’t need to change spawner.py, only write a new file as a plugin. like gckrbspawner.py
# Save this file in your site-packages directory as krbspawner.py
#
# then in /etc/jupyterhub/config.py, set:
#
# c.JupyterHub.spawner_class = 'garbage_customer.gckrbspawner.KerberosSpawner'
from jupyterhub.spawner import LocalProcessSpawner
from jupyterhub.utils import random_port
from subprocess import Popen,PIPE
from tornado import gen
import pipes
REALM = 'GC.COM'
# KerberosSpawner扩展自spawner.py的localProcessSpawner类
class KerberosSpawner(LocalProcessSpawner):
@gen.coroutine
def start(self):
"""启动子进程的方法"""
if self.ip:
self.user.server.ip = self.ip # 用户服务的ip为jupyterhub启动设置的ip
else:
self.user.server.ip = '127.0.0.1' # 或者是 127.0.0.1
self.user.server.port = random_port() # singleruser server, 也就是notebook子进程, 启动时使用随机端口
self.log.info('Spawner ip: %s' % self.user.server.ip)
self.log.info('Spawner port: %s' % self.user.server.port)
cmd = []
env = self.get_env() # 获取jupyterhub的环境变量
# self.log.info(env)
""" Get user uid and gid from linux"""
uid_args = ['id', '-u', self.user.name] # 获取当前登录的用户名对应的linux uid
uid = Popen(uid_args, stdin=PIPE, stdout=PIPE, stderr=PIPE)
uid = uid.communicate()[0].decode().strip()
gid_args = ['id', '-g', self.user.name] # 获取当前登录用户对应的 linux gid
gid = Popen(gid_args, stdin=PIPE, stdout=PIPE, stderr=PIPE)
gid = gid.communicate()[0].decode().strip()
self.log.info('UID: ' + uid + ' GID: ' + gid)
self.log.info('Authenticating: ' + self.user.name)
cmd.extend(self.cmd)
cmd.extend(self.get_args())
self.log.info("Spawning %s", ' '.join(pipes.quote(s) for s in cmd))
# 使用linux用户认证kerberos用户, 由于 jupyterhub默认使用 /home/username作为每个用户的文件夹, 所以我把用户认证需要的keytab放到每个/home/username下面
# 例如 xianglei.wb1.keytab ,对应的linux用户就是xianglei, 对应的krb用户就是 xianglei/gc-dmp-workbench1@GC.COM.
kinit = ['/usr/bin/kinit', '-kt',
'/home/%s/%s.wb1.keytab' % (self.user.name, self.user.name,),
'-c', '/tmp/krb5cc_%s' % (uid,),
'%s/gc-dmp-workbench1@%s' % (self.user.name, REALM)]
self.log.info("KRB5 initializing with command %s", ' '.join(kinit))
# 使用subprocess的Popen在spawner里面创建子进程去做krb认证
Popen(kinit, preexec_fn=self.make_preexec_fn(self.user.name)).wait()
popen_kwargs = dict(
preexec_fn=self.make_preexec_fn(self.user.name),
start_new_session=True, # 不转发 signals
)
popen_kwargs.update(self.popen_kwargs)
popen_kwargs['env'] = env
self.proc = Popen(cmd, **popen_kwargs)
self.pid = self.proc.pid
# 返回ip和端口号, 交还给jupyterhub server进行子进程服务注册
return (self.user.server.ip, self.user.server.port)
And add a config into jupyterhub generated config file
c.JupyterHub.spawner_class = 'garbage_customer.gckrbspawner.KerberosSpawner'
In next topic, I will write how to auto refresh kerberos authentication.